Ignoring the Normal pH Range for Urine Could Hurt Your Health
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
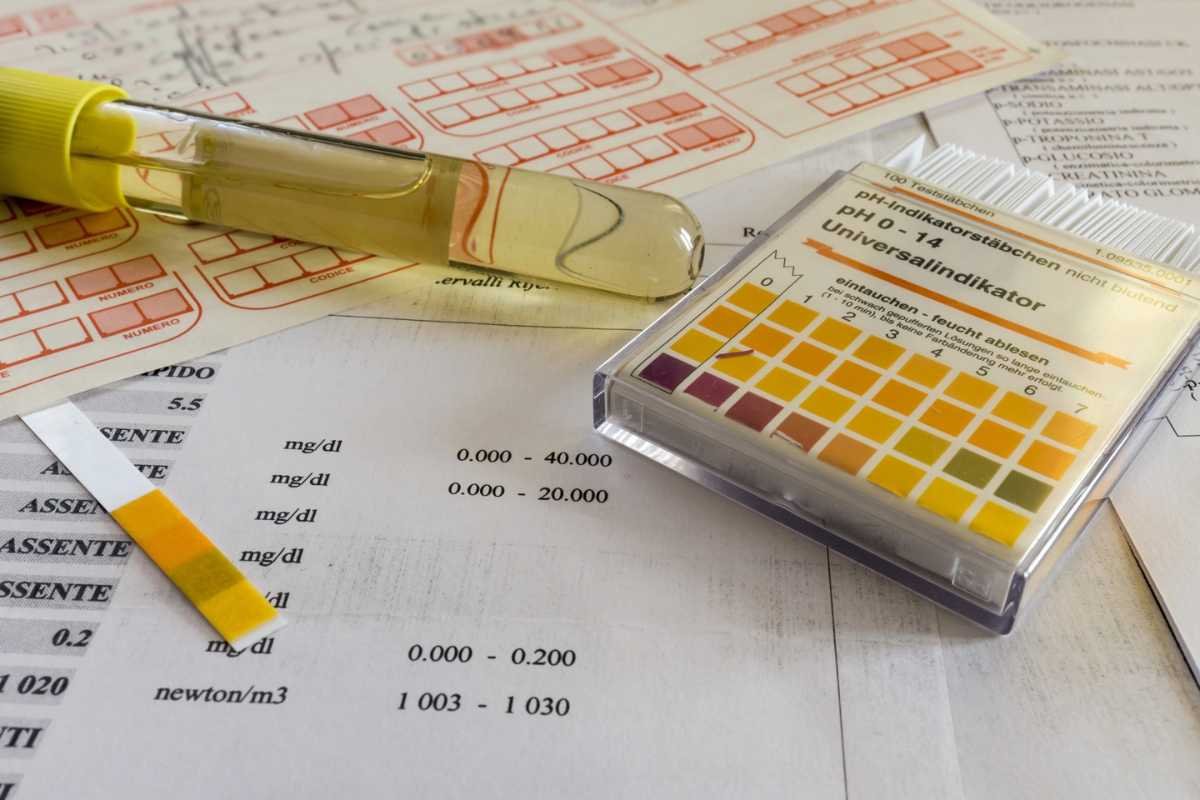
Normal pH range for urine is 4.5–8.0, averaging around 6. It indicates diet, hydration, and kidney function, and helps find out how it can be maintained and various testing methods.

- Source: blog.healthmatters.io
Your body is constantly talking to you. Are you listening?
One of the most surprising ways it does this is through your urine pH. That simple number ranging from 4.5 to 8, with most healthy adults around 6, can reveal a lot more than you might think.
From hinting at your kidney health to signalling early signs of infections or metabolic imbalances, your urine’s acidity or alkalinity acts like a subtle health dashboard. And the best part? You don’t need expensive tests to get these clues sometimes; all it takes is paying attention to what your body is already showing you. Understanding the normal pH range for urine is a powerful step toward smarter, everyday health choices.
What is Urine pH?
Simply put, pH is a measure of how acidic or alkaline a substance is. It’s measured on a scale from 0 to 14. When it comes to urine, this scale helps indicate how balanced your body’s internal environment is.
Measuring urine pH is easier than many people think. It can be done with dipstick tests at a lab, home testing kits, or through routine medical check-ups. These tests give you a quick snapshot of your body’s current state and can help spot changes before they become bigger problems.
Monitoring urine pH is about numbers as well as awareness. Tracking your urine’s acidity or alkalinity over time can provide clues about your kidney function, hydration, and early signs of infections or metabolic issues, making it a simple but powerful tool for taking charge of your health.
Normal pH Range for Urine
The normal pH range for urine typically falls between 4.5 and 8, with most healthy adults averaging around 6. This means that while urine can be slightly acidic or slightly alkaline, it usually stays near the middle of the scale.
Understanding these numbers is simple: a lower pH (closer to 4.5) indicates more acidity, while a higher pH (closer to 8) shows more alkalinity. Neither extreme is automatically dangerous, but consistently high or low values may signal underlying health issues.
It’s also important to know that urine pH naturally fluctuates throughout the day. Factors such as what you eat, how much water you drink, and even the time of day can influence your urine’s acidity or alkalinity. For example, meals rich in protein tend to make urine more acidic, while a plant-heavy diet may make it slightly more alkaline.
Typical Urine pH Range
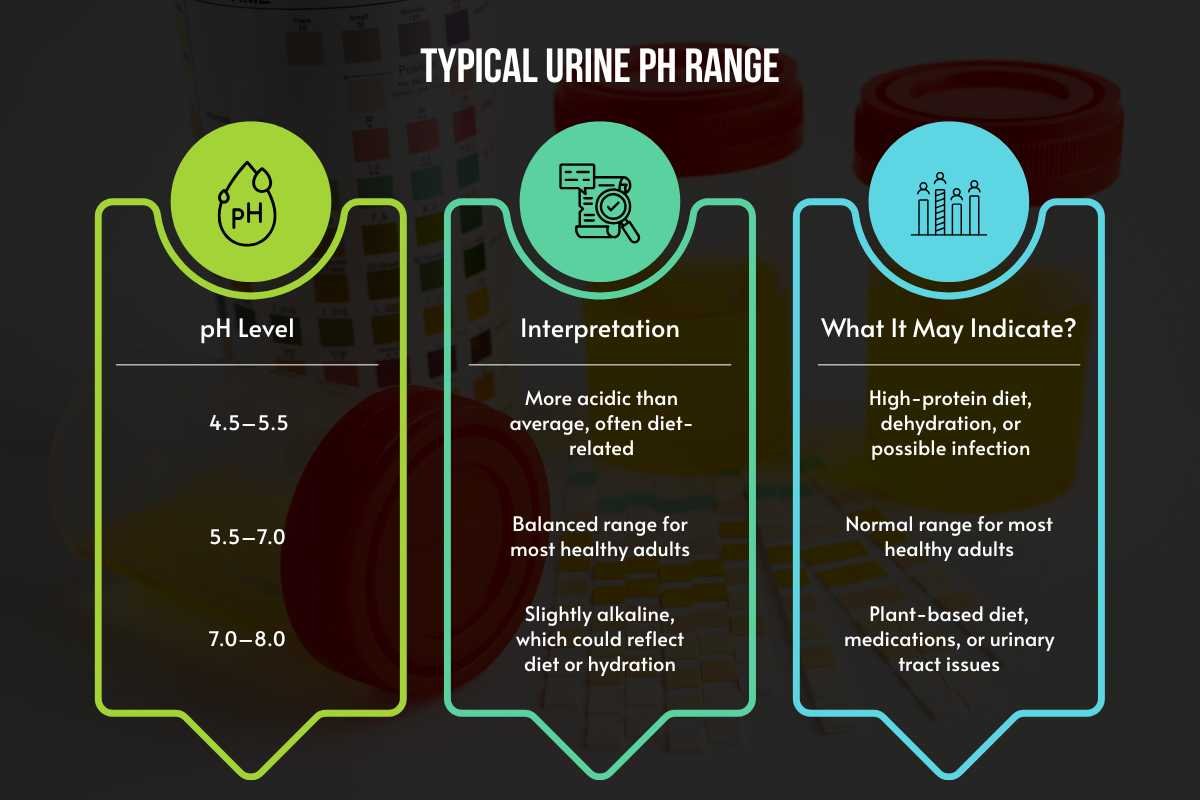
| pH Level | Interpretation | What It May Indicate? |
| 4.5–5.5 | More acidic than average, often diet-related | High-protein diet, dehydration, or possible infection |
| 5.5–7.0 | Balanced range for most healthy adults | Normal range for most healthy adults |
| 7.0–8.0 | Slightly alkaline, which could reflect diet or hydration | Plant-based diet, medications, or urinary tract issues |
Factors that Affect Urine pH
Your urine’s pH is influenced by several factors, and understanding them can help you interpret what your body is telling you. Keeping an eye on these factors can also help keep a normal pH range, which is important for overall health.
- Diet: The foods you eat directly impact urine acidity. High-protein foods like meat, fish, and eggs tend to make urine more acidic, while fruits and vegetables often make it slightly alkaline. Even small changes in your daily meals can cause temporary shifts in urine pH, which is completely normal.
- Medications & Supplements: Certain medications and supplements can alter urine pH. For example, diuretics, antacids, and vitamin C supplements can make your urine either more acidic or more alkaline. Being aware of these effects is important when trying to maintain a normal pH range for urine.
- Medical Conditions: Some health conditions can affect urine acidity. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can make urine more alkaline, while kidney stones or metabolic disorders can shift it toward acidity. Monitoring pH changes over time can provide early clues to such issues.
- Hydration Levels: How much water you drink affects urine concentration and pH. Dehydration can make urine more acidic, whereas staying well-hydrated helps keep urine pH closer to the normal, balanced range.
Why Knowing Your Urine pH Matters?
Understanding your urine’s pH isn’t just about numbers; it’s a window into your body’s health. Keeping your urine’s pH within the typical range is crucial, as it reflects your body’s internal balance and can indicate potential health issues.
1. Kidney Health and Stone Formation
The kidneys play a vital role in regulating urine pH. An imbalance can lead to the formation of kidney stones. For instance, a study highlighted that women with higher urine pH levels are more prone to developing calcium phosphate stones. This underscores the importance of monitoring urine pH to prevent such conditions.
2. Hydration and Diet’s Influence
Your daily habits significantly impact urine pH. A study found that individuals who consumed more water had a significantly lower average urine pH compared to those who didn’t, indicating better hydration. Additionally, dietary choices play a role; high-protein diets can make urine more acidic, while plant-based diets can make it more alkaline.
3. Early Detection of Infections
Changes in urine pH can signal infections. For example, urinary tract infections (UTIs) can cause urine to become more alkaline. Monitoring these changes can lead to early detection and treatment, preventing complications.
4. Overall Health Indicator
Regularly checking your urine pH can serve as an early warning system for various health issues. It can reflect your body’s acid-base balance, hydration status, and even dietary effects, helping you make informed health decisions.
How to Maintain a Healthy Urine pH?
Keeping your urine within the normal pH range for urine (4.5–8.0) is a simple yet powerful way to support overall health. Your urine pH not only reflects kidney function but also gives insight into hydration, diet, and metabolic balance. Small daily choices can make a big difference in keeping your urine pH within a healthy range.
Balance Your Diet
- Eat More Fruits and Vegetables: Foods like leafy greens, citrus fruits, and bananas are naturally alkaline and help raise urine pH toward a healthy level. According to a study in the British Journal of Nutrition, diets high in fruits and vegetables are linked to a more balanced urine pH.
- Moderate Protein Intake: While protein is essential for health, too much, especially from animal sources, can increase urine acidity. Research from The Journal of Nutrition shows that a higher dietary acid load is associated with more acidic urine.
- Practical Tip: Try to balance each meal with vegetables or fruits alongside protein-rich foods to keep your normal pH range for urine.
Stay Hydrated
- Drink Plenty of Water: Adequate hydration is one of the easiest ways to keep your urine within the usual pH range. Water dilutes urine, reducing acidity and helping the kidneys function efficiently. A study published in PMC found that higher fluid intake is linked to more balanced urine pH levels.
- Practical Tip: Aim for at least 6–8 glasses of water daily, adjusting for exercise, climate, or medical conditions, to keep your urine pH within the healthy range.
Regular Health Check-Ups
- Monitor Kidney and Metabolic Health: Routine urine tests during annual health check-ups can help you track your urine pH over time. Abnormal readings may indicate kidney issues, urinary infections, or metabolic imbalances. A study in Arthritis Research & Therapy noted that acidic urine (pH <5.0) was strongly associated with impaired kidney function.
- Practical Tip: Bring any unusual urine test results to your healthcare provider to understand whether adjustments to diet, hydration, or lifestyle are needed.
Lifestyle Factors

- Exercise and Stress Management: Regular physical activity improves metabolism and circulation, indirectly supporting a healthy urine pH. Managing stress through mindfulness, yoga, or meditation can also positively influence your body’s acid-base balance.
- Avoid Excessive Alcohol or Caffeine: High consumption of alcohol or caffeinated drinks can temporarily shift urine pH toward acidity, so moderation is key.
Urine pH Testing Methods
Checking your urine pH is a simple way to stay aware of your health and ensure it stays within the normal pH range for urine. There are several methods available, ranging from convenient home tests to more precise lab evaluations.
1. Home Testing Kits
- Convenience at Home: Urine pH test strips are widely available and easy to use. They allow you to monitor your urine pH regularly without visiting a clinic.
- How It Works: Dip the strip into a urine sample, wait for the colour to change, and compare it to the chart provided with the kit. The colour indicates whether your urine is acidic, neutral, or alkaline.
- Practical Tip: Test at the same time each day, ideally in the morning, to track trends accurately.
2. Lab Tests
- More Accurate: Lab tests provide precise readings and can detect subtle shifts in urine pH. They are often part of routine health check-ups or specific tests when a doctor suspects kidney, metabolic, or urinary issues.
- Additional Insights: Labs can also evaluate other urine parameters, such as glucose, protein, and infection markers, giving a more complete picture of your health.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Using Test Strips
- Collect a clean urine sample in a sterile container.
- Dip the pH strip into the sample for a few seconds.
- Remove and wait for the colour change, usually 30–60 seconds.
- Compare the colour to the pH chart included with the strips.
- Record the reading for future reference to track trends over time.
4. Understanding Results and When to Consult a Doctor
- Normal Range: Most healthy adults fall between pH 4.5 and 8, averaging around 6.
- When to Seek Advice: Consistently acidic (below 5) or alkaline (above 8) readings may indicate underlying health issues, such as kidney problems, urinary tract infections, or metabolic disorders. If results remain outside the normal range, consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Regular monitoring of urine pH, whether at home or through lab tests, empowers you to stay proactive about your health and keep your urine’s pH within the typical range.
Common Myths About Urine pH
When it comes to urine pH, there are several misconceptions that can confuse people about what’s normal and healthy. Understanding the facts helps you stay informed and maintain your pH range.
Myth 1: Urine Should Always Be Neutral (pH 7)
Reality: Urine pH naturally fluctuates throughout the day depending on diet, hydration, and metabolism. Most healthy adults have a pH ranging from 4.5 to 8, with an average around 6. Being slightly acidic or slightly alkaline is normal.
Myth 2: Home Test Strips Are Inaccurate
Reality: While lab tests are more precise, high-quality home pH strips can provide reliable readings if used correctly. Tracking trends over time is often more important than a single reading.
Myth 3: Acidic Urine Always Means Disease
Reality: A lower pH does not automatically indicate illness. Acidic urine can result from high-protein meals, dehydration, or even exercise. Persistent abnormal readings should be checked by a doctor, but occasional acidity is usually harmless.
Myth 4: Drinking Alkaline Water Fixes Urine pH
Reality: While alkaline water may slightly influence urine pH, overall diet, hydration, and kidney function have a much bigger impact. Relying solely on alkaline water is not a guaranteed way to maintain a healthy urine pH.
Myth 5: Urine pH Reflects Overall Blood pH
Reality: Urine pH shows how your body is excreting acids or bases, but it does not directly indicate blood pH. Blood pH is tightly regulated and usually remains within a narrow range.
Understanding the truth behind these myths helps you interpret your urine pH correctly and stay within the normal pH range for urine, supporting better kidney function, hydration, and overall health.
Conclusion
The normal pH range for urine may seem like a small detail, but it tells a big story about your health. From diet and hydration to kidney function and infections, urine pH can reveal early signs of imbalance that are worth paying attention to.
By making mindful choices like eating more fruits and vegetables, staying hydrated, and going for regular check-ups, you can keep your urine pH within a healthy range. Home testing strips make it easier than ever to track changes, but remember: it’s the long-term trends that matter most, not just one reading.
If your results consistently fall outside the normal pH range, it’s a good idea to consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation. Small adjustments today can go a long way in protecting your kidney health and overall well-being tomorrow.
Your body gives you signals every day; listening to them through simple checks like urine pH testing is one of the smartest steps toward preventive health.
FAQs
1. What is the normal pH range for urine?
The normal pH range is between 4.5 and 8.0, with most healthy adults averaging around 6. This slightly acidic level helps the kidneys maintain the body’s natural balance.
2. What does it mean if my urine pH is too low or too high?
If urine pH drops below 5, it may suggest dehydration, a high-protein diet, or kidney-related issues. A reading above 8 can point to urinary tract infections or the effect of certain medications.
3. Can diet affect the normal pH range for urine?
Yes, diet plays a major role. High-protein foods like meat and fish lower urine pH (making it acidic), while vegetables and fruits raise it (making it more alkaline). Drinking enough water also helps keep the balance.
4. How can I test my urine pH at home?
You can easily test with urine pH strips available at pharmacies. Dip the strip in fresh urine, wait for the colour change, and compare it with the chart to check where you fall within the normal pH range for urine.
5. When should I see a doctor about urine pH?
Occasional changes are normal, but consistently acidic or alkaline results may indicate an underlying condition like kidney stones, UTIs, or metabolic issues. In such cases, consulting a healthcare provider is important.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment